Fibroma
Fibroma. Plantar fibromas are small — usually less than an inch — and grow on the arch of your foot. Fibromas can form anywhere in the body and usually do not require treatment or removal.
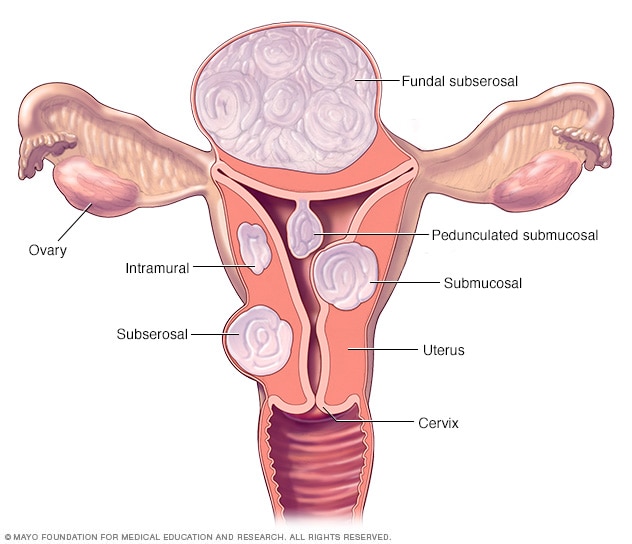
A fibroma is typically a benign fibroid or fibroid tumor. An oral fibroma is a type of mouth sore that consists of localized connective tissue that becomes irritated and inflamed. Fibromas most often appear inside the cheeks, on the.
It develops in the plantar fascia, which is thick, fibrous tissue at.
A fibroma is typically a benign fibroid or fibroid tumor. It is distinguished histologically by the lack of giant cells, foamy histiocytes and synovial cells. [noun] a benign tumor consisting mainly of fibrous tissue.
Most common ovarian stromal tumor.
• the reason for the occurrence of this uncontrolled cell growth is unknown but sometimes it occurs as a result of injury or local irritation. Fibromas are composed of fibrous, or connective, tissue. Oral fibroma can be pink or white and are generally smooth and raised.
A plantar fibroma is a fibrous knot, or nodule, in the arch of the foot.
Ameloblastic fibroma an odontogenic fibroma, marked by simultaneous proliferation of both epithelial and mesenchymal tissue, without formation of enamel or dentin. It is usually the same colour as the rest of the mouth lining but is sometimes paler or, if it has bled, may look a dark colour. Fibromas can be found in many places in the body.
It has a range of potential causes including genetics and.
Made up of fibrous connective tissue rather than cancerous cells, they can grow in any and all organs and usually do not require removal. An oral fibroma is a type of mouth sore that consists of localized connective tissue that becomes irritated and inflamed. While discovering a new growth within your mouth can be alarming at first.
The ovarian fibroma is a benign tumor composed of fibroblasts and collagen fibers.
The surface may be ulcerated due to trauma, or become rough and scaly. A definitive surgical protocol has not yet been published. Let's go over what this common lesion is, how it's found, and recommendations for prevention and treatment.
Comments
Post a Comment